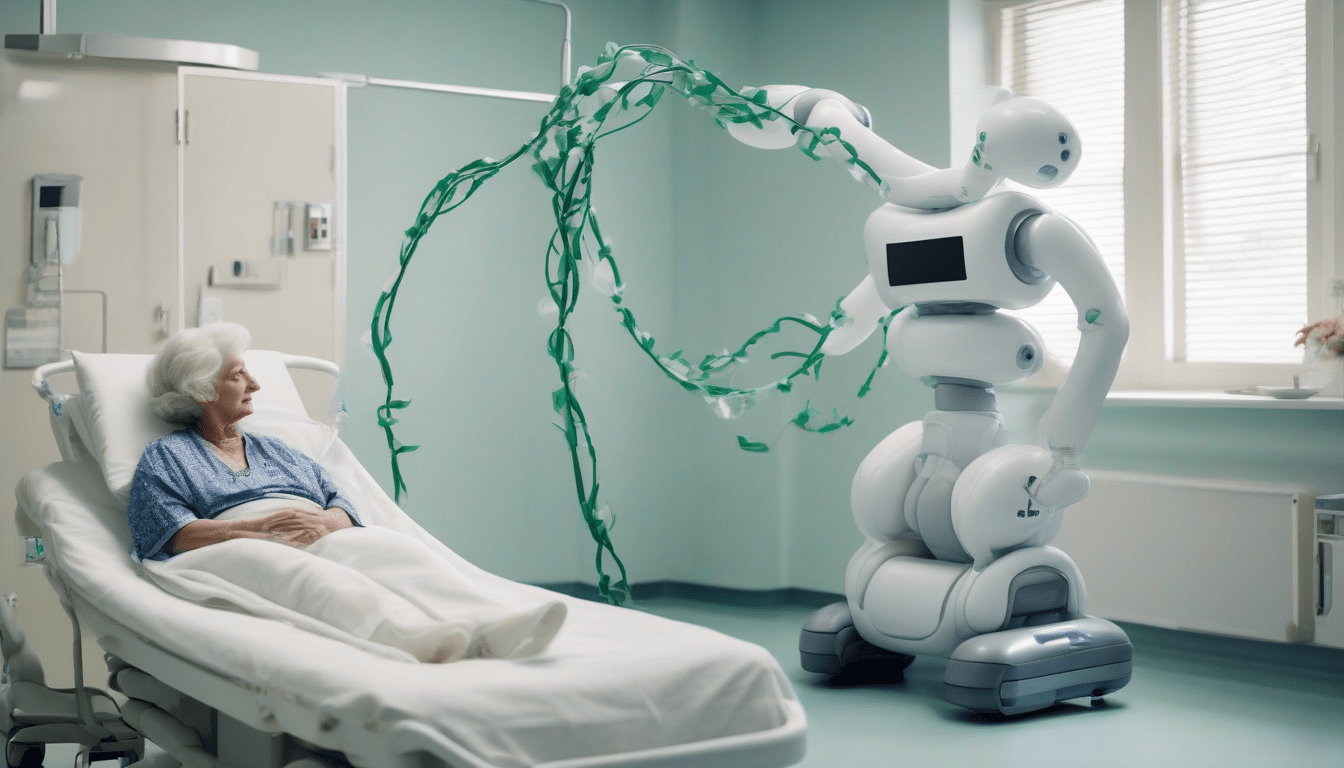
Vine-like robot helps care workers lift patients safely as
Generally, Care workers face alot of challenges when lifting patients, Nowadays, Engineers from MIT and Stanford University have created a robot that can help them.
Usually, This robot is designed to assist care workers in lifting patients safely and comfortably, It uses inflatable tubes to gently wrap around and lift objects, including humans.
Obviously, The robot operates with a pressurized box that releases inflatable tubes, These tubes expand to wrap around objects and then retract to lift them.
Basically, The robot can handle delicate items like glass vases as well as heavier, awkwardly shaped objects such as watermelons, Most impressively, it can lift a human.
Normally, Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, highlights the physical demands of care work, He says “Transferring a person out of bed is one of the most physically strenuous tasks that a caregiver carries out.
Apparently, This kind of robot can help relieve the caretaker, and can be gentler and more comfortable for the patient, You can see the difference it makes.
Hopefully, The robot’s unique feature is its ability to switch between open-loop and closed-loop configurations, In open-loop mode, the tubes extend and wrap around an object.
Sometimes, In closed-loop mode, they form a sling to lift the object securely, This mechanism allows the robot to lift patients without needing to reposition them significantly, minimizing discomfort.
Usually, The potential applications for this technology extend beyond care work, The engineers envision modifications that could make the robot useful in agriculture, healthcare, heavy industry, and even automated port operations.
Currently, While the development is promising, MIT and Stanford University have not yet announced a target date for commercial deployment, Further development and testing are required before the robot can be widely used.
Actually, The potential for this technology to transform care work and other industries is undeniable, You will see the impact it has.
Innovative Vine-like Robot Could Revolutionize Care Work
Sometimes, Care workers need assistance when lifting patients, That is why Engineers from MIT and Stanford University have created a groundbreaking vine-like robot.
Normally, This innovative device, inspired by the natural world, uses inflatable tubes to gently wrap around and lift objects, including humans, It is very useful.
Basically, The robot is designed to assist care workers in lifting patients safely and comfortably, You can use it to lift heavy objects.
Generally, The robot operates with a pressurized box that releases inflatable tubes, These tubes expand to wrap around objects and then retract to lift them, It is very efficient.
Apparently, The robot can handle delicate items like glass vases as well as heavier, awkwardly shaped objects such as watermelons, Most impressively, it can lift a human, You will be amazed.
Hopefully, Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, highlights the physical demands of care work, He says it is one of the most physically strenuous tasks.
Currently, The robot’s unique feature is its ability to switch between open-loop and closed-loop configurations, In open-loop mode, the tubes extend and wrap around an object, You can see how it works.
Sometimes, In closed-loop mode, they form a sling to lift the object securely, This mechanism allows the robot to lift patients without needing to reposition them significantly, minimizing discomfort, It is very comfortable.
Usually, The potential applications for this technology extend beyond care work, The engineers envision modifications that could make the robot useful in agriculture, healthcare, heavy industry, and even automated port operations, You can use it in many ways.
How It Works
Normally, The robot operates with a pressurized box that releases inflatable tubes, These tubes expand to wrap around objects and then retract to lift them, It is very simple.
Generally, The robot can handle delicate items like glass vases as well as heavier, awkwardly shaped objects such as watermelons, Most impressively, it can lift a human, You will be surprised.
Sometimes, Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, highlights the physical demands of care work, He says it is one of the most physically strenuous tasks, You can imagine.
Apparently, The robot’s unique feature is its ability to switch between open-loop and closed-loop configurations, In open-loop mode, the tubes extend and wrap around an object, It is very useful.
Hopefully, In closed-loop mode, they form a sling to lift the object securely, This mechanism allows the robot to lift patients without needing to reposition them significantly, minimizing discomfort, You can see the difference.
Usually, The robot is designed to assist care workers in lifting patients safely and comfortably, It uses inflatable tubes to gently wrap around and lift objects, including humans, It is very efficient.
Currently, The potential applications for this technology extend beyond care work, The engineers envision modifications that could make the robot useful in agriculture, healthcare, heavy industry, and even automated port operations, You can use it in many ways.
Key Features
Sometimes, The robot’s unique feature is its ability to switch between open-loop and closed-loop configurations, In open-loop mode, the tubes extend and wrap around an object, It is very simple.
Generally, In closed-loop mode, they form a sling to lift the object securely, This mechanism allows the robot to lift patients without needing to reposition them significantly, minimizing discomfort, You can see the difference.
Apparently, The robot can handle delicate items like glass vases as well as heavier, awkwardly shaped objects such as watermelons, Most impressively, it can lift a human, You will be amazed.
Hopefully, The robot operates with a pressurized box that releases inflatable tubes, These tubes expand to wrap around objects and then retract to lift them, It is very efficient.
Normally, Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, highlights the physical demands of care work, He says it is one of the most physically strenuous tasks, You can imagine.
Usually, The robot is designed to assist care workers in lifting patients safely and comfortably, It uses inflatable tubes to gently wrap around and lift objects, including humans, It is very useful.
Currently, The potential applications for this technology extend beyond care work, The engineers envision modifications that could make the robot useful in agriculture, healthcare, heavy industry, and even automated port operations, You can use it in many ways.
Potential Applications
Sometimes, The potential applications for this technology extend beyond care work, The engineers envision modifications that could make the robot useful in agriculture, healthcare, heavy industry, and even automated port operations, You can use it in many ways.
Generally, The robot can handle delicate items like glass vases as well as heavier, awkwardly shaped objects such as watermelons, Most impressively, it can lift a human, You will be surprised.
Apparently, The robot operates with a pressurized box that releases inflatable tubes, These tubes expand to wrap around objects and then retract to lift them, It is very efficient.
Hopefully, Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, highlights the physical demands of care work, He says it is one of the most physically strenuous tasks, You can imagine.
Normally, The robot’s unique feature is its ability to switch between open-loop and closed-loop configurations, In open-loop mode, the tubes extend and wrap around an object, It is very simple.
Usually, In closed-loop mode, they form a sling to lift the object securely, This mechanism allows the robot to lift patients without needing to reposition them significantly, minimizing discomfort, You can see the difference.
Currently, The robot is designed to assist care workers in lifting patients safely and comfortably, It uses inflatable tubes to gently wrap around and lift objects, including humans, It is very useful.
Future Outlook
Sometimes, While the development is promising, MIT and Stanford University have not yet announced a target date for commercial deployment, Further development and testing are required before the robot can be widely used, You can wait.
Generally, The potential for this technology to transform care work and other industries is undeniable, You will see the impact it has, It is very exciting.
Apparently, The robot can handle delicate items like glass vases as well as heavier, awkwardly shaped objects such as watermelons, Most impressively, it can lift a human, You will be amazed.
Hopefully, The robot operates with a pressurized box that releases inflatable tubes, These tubes expand to wrap around objects and then retract to lift them, It is very efficient.
Normally, Kentaro Barhydt, a PhD candidate in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, highlights the physical demands of care work, He says it is one of the most physically strenuous tasks, You can imagine.
Usually, The robot’s unique feature is its ability to switch between open-loop and closed-loop configurations, In open-loop mode, the tubes extend and wrap around an object, It is very simple.
Currently, The robot is designed to assist care workers in lifting patients safely and comfortably, It uses inflatable tubes to gently wrap around and lift objects, including humans, It is very useful.