Two Rocket Failures Highlight Ongoing Space Challenges
Generally, Space travel is getting more interesting every year, You are seeing companies like SpaceX making it look pretty easy. Obviously, two rocket failures on December 22 serve as a reminder that sending rockets into space is still pretty complex.
Usually, People think that space travel is all about launching a rocket and hoping for the best, But it is not that simple. Apparently, You need to consider a lot of factors before launching a rocket into space.
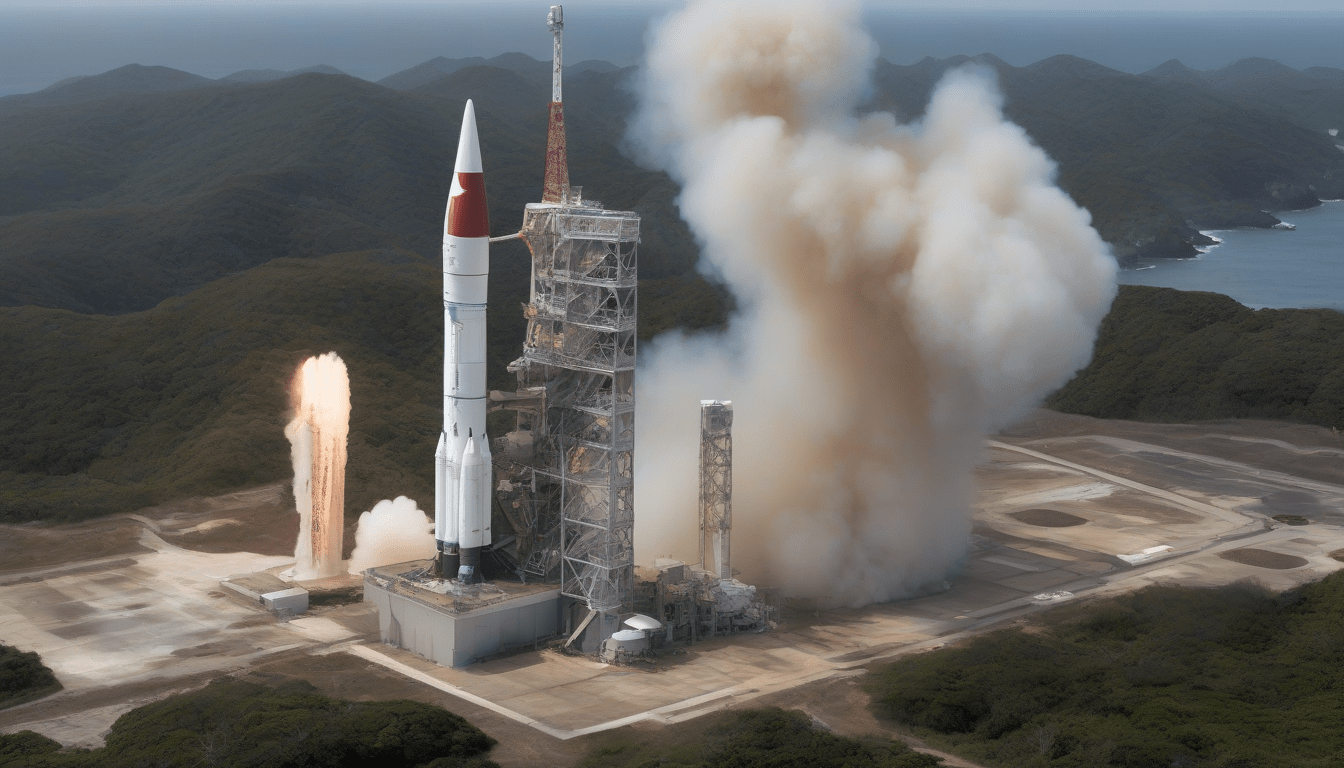
Basically, The first failure involved the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and its H3 rocket, Which was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center. Normally, The mission aimed to deploy the Quasi‑Zenith Satellite System (QZS‑5), But it did not go as planned.
Unfortunately, The second‑stage engine failed to ignite properly, causing the satellite to miss its intended orbit, And this is not the first time this has happened.
Understanding The Challenges
Normally, When You look at the details of the failure, You realize that the initial stages of the launch went smoothly, But the second-stage engine was the problem. Apparently, This incident marks the second consecutive issue for the H3 rocket, And it is raising concerns about its reliability.
Usually, You would expect a rocket like the H3 to be more reliable, But it seems like there are still some issues that need to be addressed.
JAXA H3 Rocket Failure
Generally, The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is still trying to figure out what went wrong with its H3 rocket, And it is not an easy task. Obviously, The agency has to consider a lot of factors before it can determine the cause of the failure.
Usually, The investigation process takes a lot of time, And it requires a lot of expertise.
South Korean Hanbit‑Nano Rocket Failure
Basically, The second failure occurred with the South Korean Hanbit‑Nano rocket, Which was launched from Brazil’s Alcântara Space Center. Normally, The mission, operated by Innospace, encountered problems shortly after liftoff, Around the time the rocket experienced maximum aerodynamic stress, known as Max Q.
Apparently, The payload included small satellites from Brazil, India, and South Korea, intended for technology development, education, and environmental data collection.
Usually, You would expect a mission like this to be a success, But it seems like there were some technical issues that could not be resolved.
Implications for the Space Industry
Generally, These failures underscore the technological precision required for successful rocket launches, And it is a big challenge. Obviously, Even small anomalies can lead to mission failures, highlighting the inherent risks and challenges of space travel.
Normally, Companies like SpaceX have achieved high reliability with their rockets, But the industry as a whole continues to face significant technical hurdles.
Usually, You need to be very careful when launching a rocket into space, Because the consequences of a failure can be severe.
Generally, Despite the advancements in space technology, the recent failures of the Japanese H3 and South Korean Hanbit‑Nano rockets remind us that space travel is still far from being a straightforward task.
Apparently, These incidents highlight the need for continued innovation and problem‑solving to overcome the complexities of rocket science, And it is not going to be easy.