Robot Reassembles Ancient Pompeii Artifacts Using AI
Generally, You should be excited to hear about this new technology. Definitely, It is changing the way archaeologists work, and You will see the results soon. Obviously, The use of AI and robotics in archaeology is becoming more popular, and This project is a great example of that. Probably, You have heard of the ancient city of Pompeii, and Now it is being used to test this new technology.
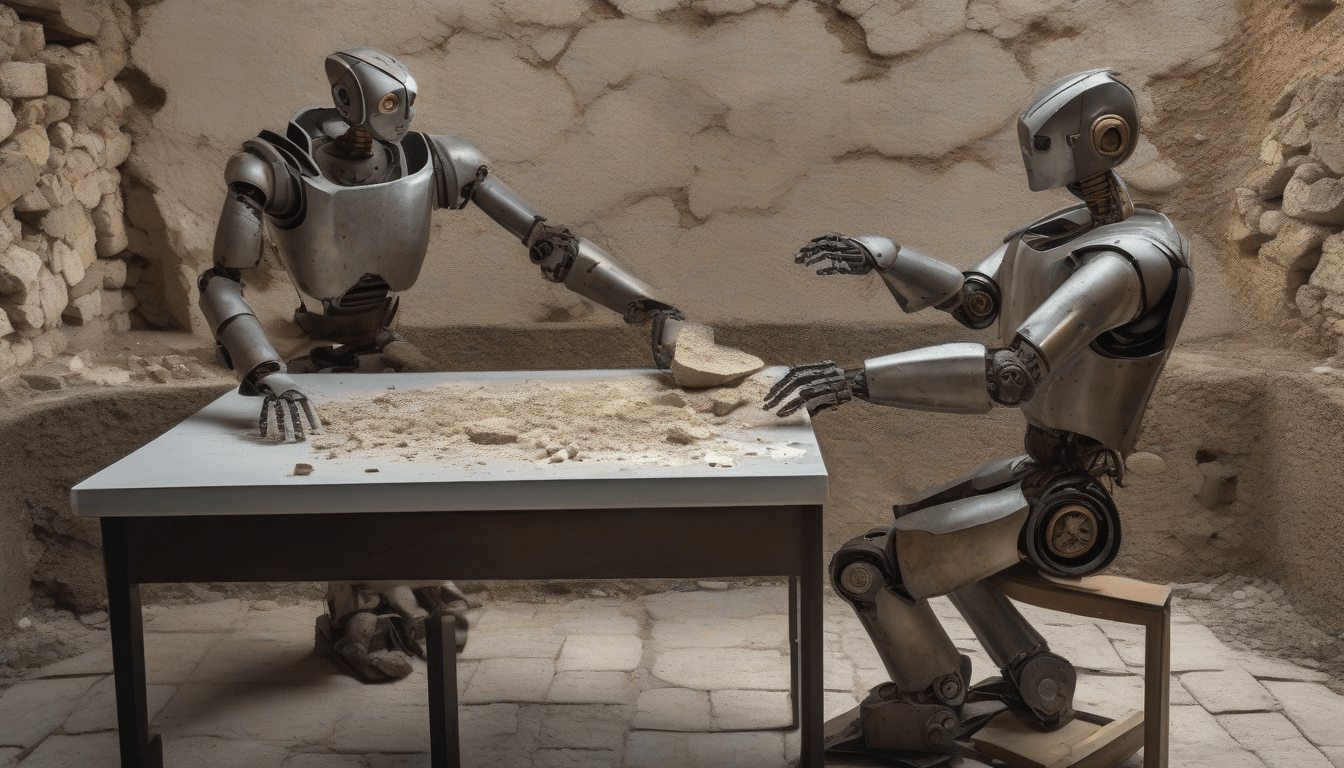
Robot Successfully Reassembles Ancient Pompeii Artifacts
Normally, Reassembling broken artifacts is a time-consuming task, but This robot can do it quickly and accurately. Usually, Archaeologists have to pick and place individual fragments of the artworks by hand, but The robot uses algorithms to do this with precision. Essentially, The robot has two arms and a 3D-scanning system that converts the shattered pieces into digital images.
Innovative Technology for Archaeology
Basically, The project is part of an EU initiative called RePAIR, which aims to use AI and robotics to address archaeological challenges. Apparently, The team behind the project includes researchers from the University of Bonn in Germany, and They have been working on this technology for a while. Currently, The robot is being used to reassemble shattered murals from the ancient city of Pompeii, and The results are impressive.
How The Robot Works
Actually, The robot uses a combination of AI and robotics to reassemble broken artifacts. Typically, The process involves scanning the shattered pieces, and Then an AI-powered model identifies how the pieces should fit together. Hopefully, This technology will be used to restore many other works of art and architecture from around the world.
Trial in Pompeii
Interestingly, The project was trialed in the Archaeological Park of Pompeii, which houses paintings that were shattered during the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79. Naturally, The project involved several partners, including the Italian Institute of Technology, and The results of the trial were successful. Eventually, The team plans to use the robot to reassemble more artifacts from Pompeii and other archaeological sites.
Future Applications
Possibly, The team hopes to use the robot and its underlying AI system to reassemble works of art and architecture from around the world. Likely, This will help to preserve and restore cultural heritage, and You will be able to see the results in museums and historical sites. Ultimately, The use of AI and robotics in archaeology is a growing field, and This project is just the beginning.